
GE Aerospace (GE)
GE Aerospace is a compelling stock. Its marriage of growth and profitability makes it a financial powerhouse with attractive upside.― StockStory Analyst Team
1. News
2. Summary
Why We Like GE Aerospace
One of the original 12 companies on the Dow Jones Industrial Average, General Electric (NYSE:GE) is a multinational conglomerate providing technologies for various sectors including aviation, power, renewable energy, and healthcare.
- Earnings growth has massively outpaced its peers over the last five years as its EPS has compounded at 34.7% annually
- Powerful free cash flow generation enables it to reinvest its profits or return capital to investors consistently
- ROIC punches in at 29.1%, illustrating management’s expertise in identifying profitable investments


We see a bright future for GE Aerospace. No coincidence the stock is up 260% over the last five years.
Is Now The Time To Buy GE Aerospace?
Is Now The Time To Buy GE Aerospace?
At $319.65 per share, GE Aerospace trades at 46.6x forward P/E. There’s no denying that the lofty valuation means there’s much good news priced into the stock.
If you like the company and believe the bull case, we suggest making it a smaller position as our analysis shows high-quality companies outperform the market over a multi-year period regardless of valuation.
3. GE Aerospace (GE) Research Report: Q4 CY2025 Update
Industrial conglomerate GE Aerospace (NYSE:GE) beat Wall Street’s revenue expectations in Q4 CY2025, with sales up 17.6% year on year to $12.72 billion. Its non-GAAP profit of $1.57 per share was 9.5% above analysts’ consensus estimates.
GE Aerospace (GE) Q4 CY2025 Highlights:
- Revenue: $12.72 billion vs analyst estimates of $11.18 billion (17.6% year-on-year growth, 13.8% beat)
- Adjusted EPS: $1.57 vs analyst estimates of $1.43 (9.5% beat)
- Adjusted EPS guidance for the upcoming financial year 2026 is $7.25 at the midpoint, beating analyst estimates by 1.8%
- Operating Margin: 17.9%, in line with the same quarter last year
- Free Cash Flow Margin: 13.8%, similar to the same quarter last year
- Market Capitalization: $336 billion
Company Overview
One of the original 12 companies on the Dow Jones Industrial Average, General Electric (NYSE:GE) is a multinational conglomerate providing technologies for various sectors including aviation, power, renewable energy, and healthcare.
GE Aerospace (GE) was founded in 1892 through the merger of Edison General Electric Company, established by Thomas Edison, and Thomson-Houston Electric Company. This merger brought together several of Edison's early businesses, creating a diversified technology and manufacturing organization. Over the decades, GE expanded into numerous sectors, including lighting, industrial products, power generation, and later, aviation and healthcare.
Throughout the 20th century, GE was known for its innovation in various fields, including the introduction of the first U.S. jet engine in the 1940s and significant advancements in medical imaging technology. In recent years, GE has streamlined its operations to focus more intensely on high-performing sectors such as aviation, power generation, and renewable energy, while divesting from less core businesses like NBC Universal and its Appliances division. Additionally in line with its streamlining efforts, in 2023, GE spun-off its healthcare segment into GE HealthCare.
GE Aerospace operations can logically be broken down into three categories: aerospace, renewable energy, and power. In aerospace, GE is renowned for its production of commercial and military aircraft engines, with products from CFM International and Engine Alliance. These include engines for narrowbody, widebody, and regional airframes, complemented by extensive maintenance, repair, and overhaul services, and the sale of spare parts.
In renewable energy, GE’s portfolio includes onshore and offshore wind technologies, hydroelectric solutions, battery storage, and hybrid systems aimed at advancing global energy transition. The company not only manufactures wind turbines and related technology but also offers services that enhance the operational efficiency and capacity of wind farms through digital platforms. The Power segment focuses on producing a broad spectrum of technologies for energy production, including gas and steam turbines, and power conversion systems, catering to diverse industries from utilities to transportation.
GE generates revenue through the sale of its industrial equipment and services. A significant portion of GE's revenue also comes from recurring sources, such as long-term service agreements, maintenance, repair, and overhaul services, and the sale of spare parts. These services are essential for maintaining the extensive installed base of GE's equipment worldwide, ensuring a steady stream of revenue beyond the initial sale.
General Electric has announced a strategic plan to split into three distinct public companies to enhance focus and market agility within its diversified portfolio. The plan includes forming GE Aerospace from its existing Aerospace business, combining Renewable Energy and Power into a single entity named GE Vernova, and spinning off its HealthCare business, which it completed in 2023, into a separate company.
4. General Industrial Machinery
Automation that increases efficiency and connected equipment that collects analyzable data have been trending, creating new demand for general industrial machinery companies. Those who innovate and create digitized solutions can spur sales and speed up replacement cycles, but all general industrial machinery companies are still at the whim of economic cycles. Consumer spending and interest rates, for example, can greatly impact the industrial production that drives demand for these companies’ offerings.
Competitors offering similar products include Siemens AG (NYSE:SIE), Honeywell International (NYSE:HON), and Raytheon Technologies (NYSE:RTX).
5. Revenue Growth
Examining a company’s long-term performance can provide clues about its quality. Any business can experience short-term success, but top-performing ones enjoy sustained growth for years. Over the last five years, GE Aerospace grew its sales at an incredible 15.8% compounded annual growth rate. Its growth surpassed the average industrials company and shows its offerings resonate with customers, a great starting point for our analysis.
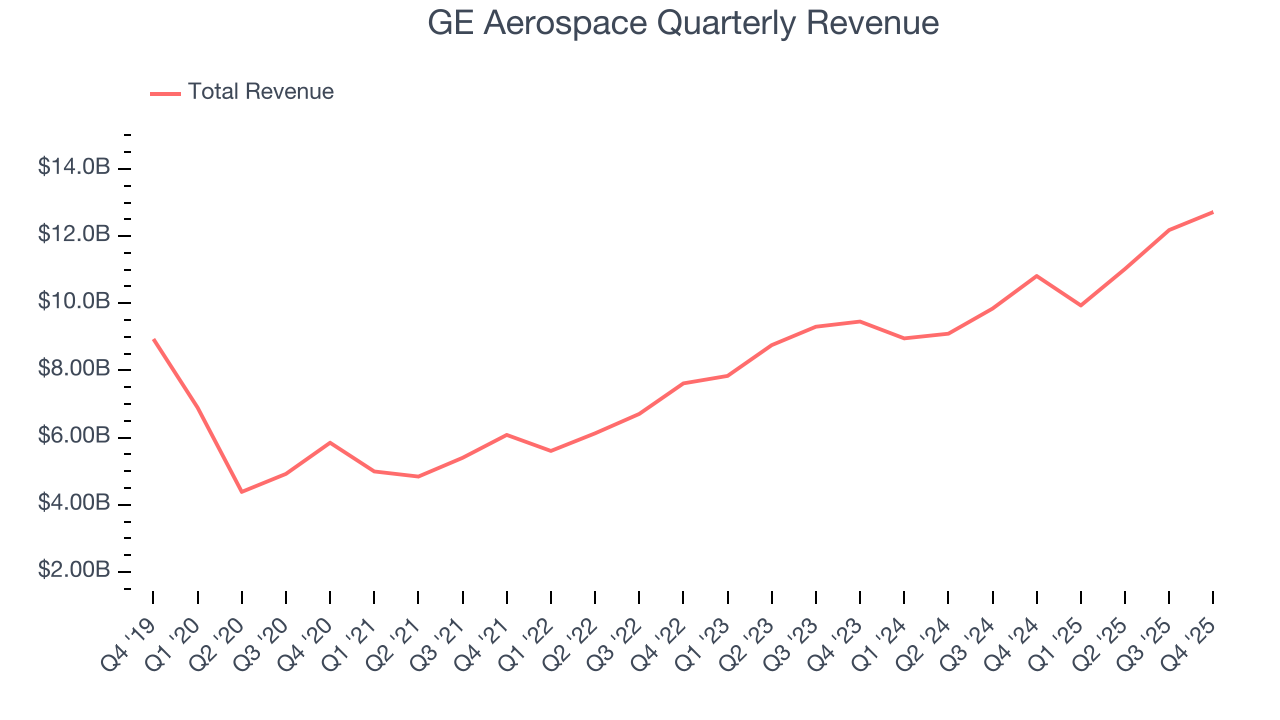
Long-term growth is the most important, but within industrials, a half-decade historical view may miss new industry trends or demand cycles. GE Aerospace’s annualized revenue growth of 13.9% over the last two years is below its five-year trend, but we still think the results suggest healthy demand. 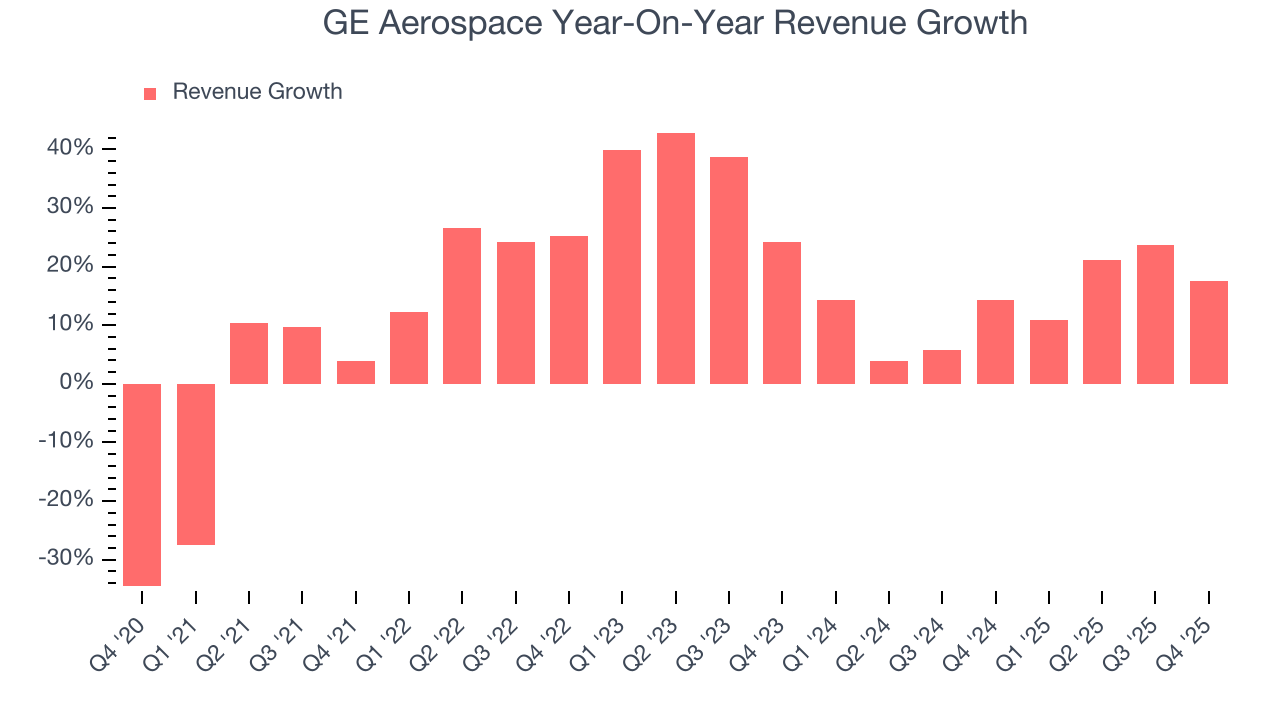
This quarter, GE Aerospace reported year-on-year revenue growth of 17.6%, and its $12.72 billion of revenue exceeded Wall Street’s estimates by 13.8%.
Looking ahead, sell-side analysts expect revenue to grow 1% over the next 12 months, a deceleration versus the last two years. This projection is underwhelming and indicates its products and services will face some demand challenges. At least the company is tracking well in other measures of financial health.
6. Gross Margin & Pricing Power
GE Aerospace has bad unit economics for an industrials business, signaling it operates in a competitive market. As you can see below, it averaged a negative 23.2% gross margin over the last five years. That means GE Aerospace lost $23.24 for every $100 in revenue. 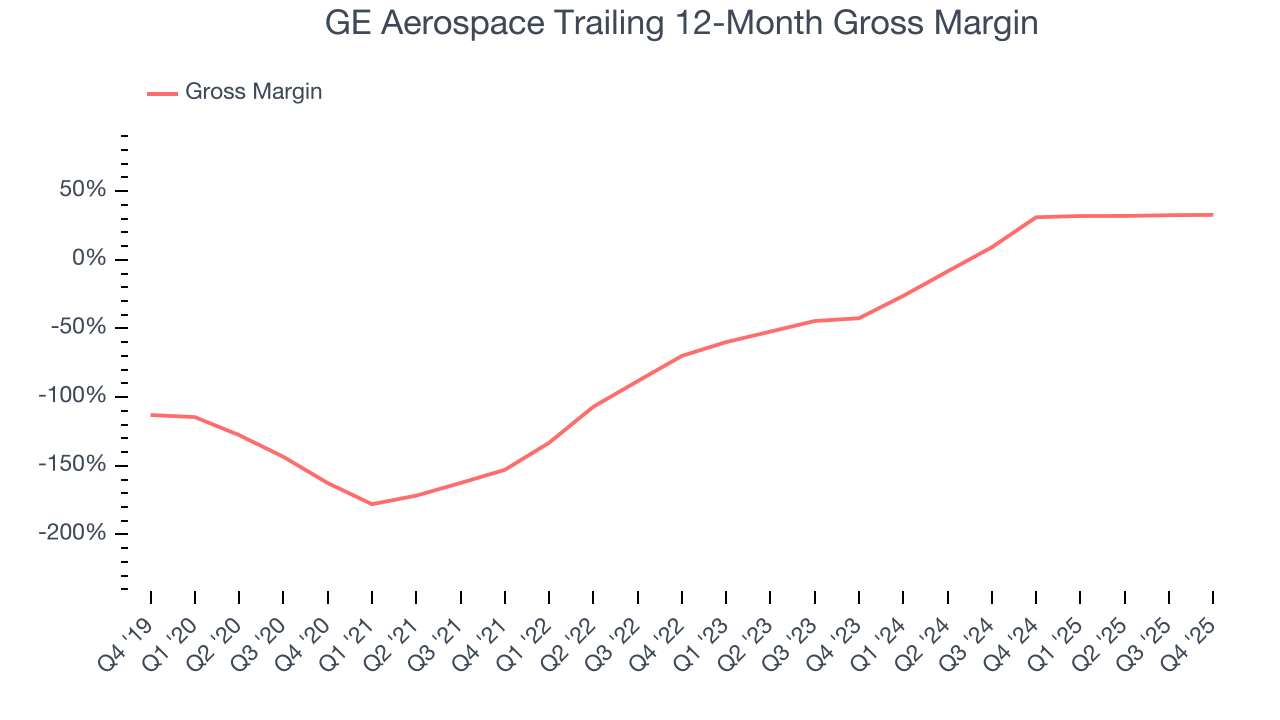
GE Aerospace’s gross profit margin came in at 34.2% this quarter, in line with the same quarter last year. Zooming out, GE Aerospace’s full-year margin has been trending up over the past 12 months, increasing by 1.7 percentage points. If this move continues, it could suggest better unit economics due to more leverage from its growing sales on the fixed portion of its cost of goods sold (such as manufacturing expenses).
7. Operating Margin
Operating margin is a key measure of profitability. Think of it as net income - the bottom line - excluding the impact of taxes and interest on debt, which are less connected to business fundamentals.
GE Aerospace has been a well-oiled machine over the last five years. It demonstrated elite profitability for an industrials business, boasting an average operating margin of 17.7%. This result was particularly impressive because of its low gross margin, which is mostly a factor of what it sells and takes huge shifts to move meaningfully. Companies have more control over their operating margins, and it’s a show of well-managed operations if they’re high when gross margins are low.
Looking at the trend in its profitability, GE Aerospace’s operating margin rose by 6.2 percentage points over the last five years, as its sales growth gave it immense operating leverage.
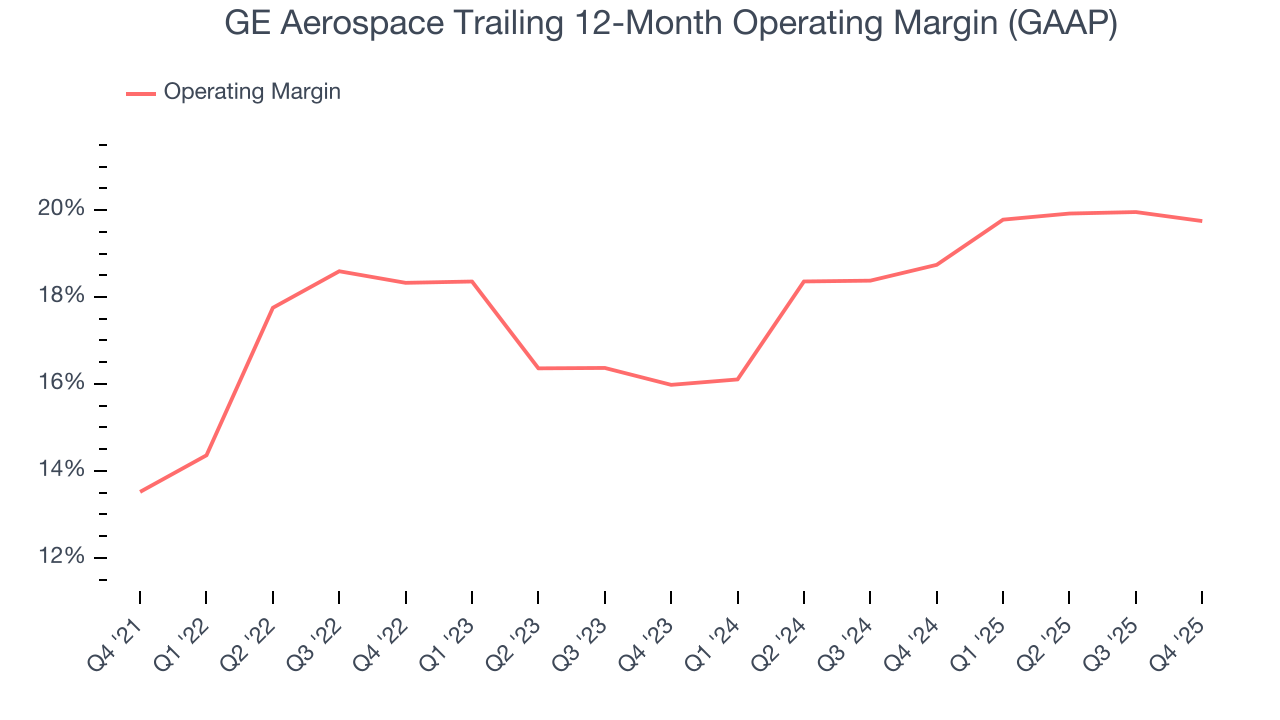
This quarter, GE Aerospace generated an operating margin profit margin of 17.9%, in line with the same quarter last year. This indicates the company’s cost structure has recently been stable.
8. Earnings Per Share
Revenue trends explain a company’s historical growth, but the long-term change in earnings per share (EPS) points to the profitability of that growth – for example, a company could inflate its sales through excessive spending on advertising and promotions.
GE Aerospace’s EPS grew at an astounding 79.3% compounded annual growth rate over the last five years, higher than its 15.8% annualized revenue growth. This tells us the company became more profitable on a per-share basis as it expanded.
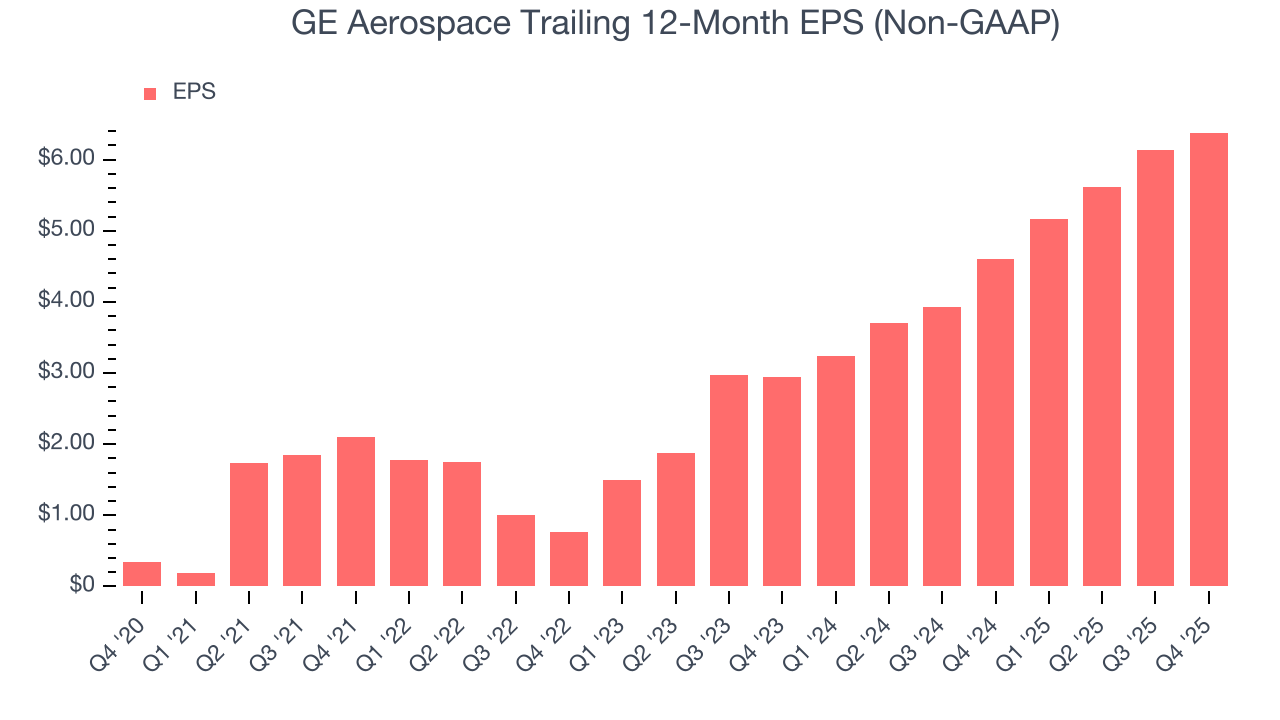
Diving into the nuances of GE Aerospace’s earnings can give us a better understanding of its performance. As we mentioned earlier, GE Aerospace’s operating margin was flat this quarter but expanded by 6.2 percentage points over the last five years. On top of that, its share count shrank by 4.4%. These are positive signs for shareholders because improving profitability and share buybacks turbocharge EPS growth relative to revenue growth. 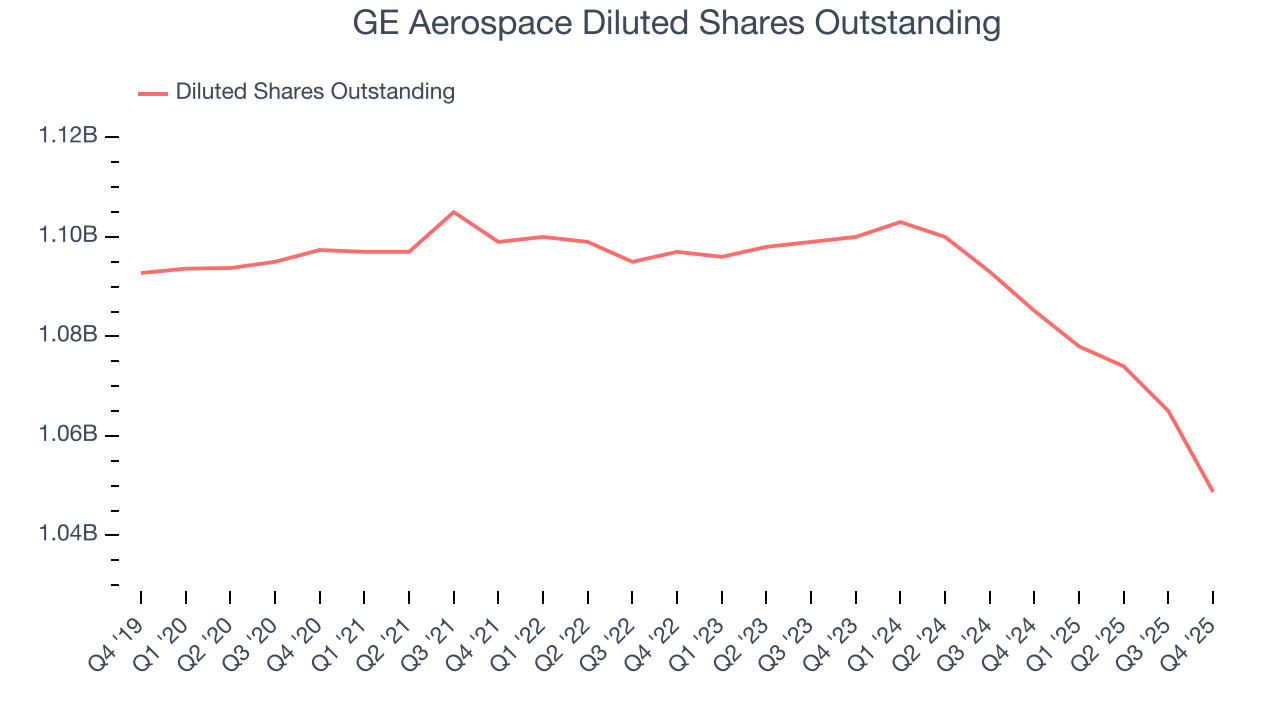
Like with revenue, we analyze EPS over a more recent period because it can provide insight into an emerging theme or development for the business.
For GE Aerospace, its two-year annual EPS growth of 47.1% was lower than its five-year trend. We still think its growth was good and hope it can accelerate in the future.
In Q4, GE Aerospace reported adjusted EPS of $1.57, up from $1.32 in the same quarter last year. This print beat analysts’ estimates by 9.8%. Over the next 12 months, Wall Street expects GE Aerospace’s full-year EPS of $6.38 to grow 10.4%.
9. Cash Is King
Although earnings are undoubtedly valuable for assessing company performance, we believe cash is king because you can’t use accounting profits to pay the bills.
GE Aerospace has shown terrific cash profitability, putting it in an advantageous position to invest in new products, return capital to investors, and consolidate the market during industry downturns. The company’s free cash flow margin was among the best in the industrials sector, averaging 15.3% over the last five years.
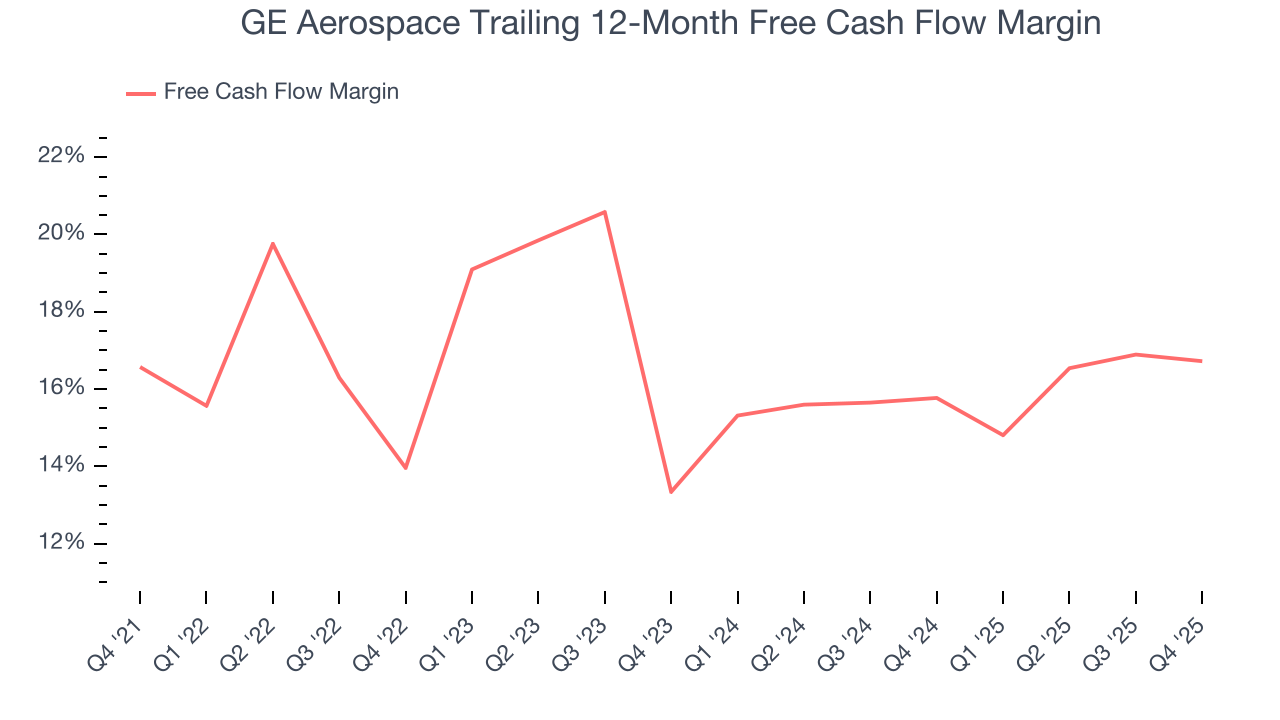
GE Aerospace’s free cash flow clocked in at $1.76 billion in Q4, equivalent to a 13.8% margin. This cash profitability was in line with the comparable period last year but below its five-year average. We wouldn’t read too much into it because investment needs can be seasonal, leading to short-term swings. Long-term trends trump temporary fluctuations.
10. Return on Invested Capital (ROIC)
EPS and free cash flow tell us whether a company was profitable while growing its revenue. But was it capital-efficient? Enter ROIC, a metric showing how much operating profit a company generates relative to the money it has raised (debt and equity).
GE Aerospace’s five-year average ROIC was 25%, placing it among the best industrials companies. This illustrates its management team’s ability to invest in highly profitable ventures and produce tangible results for shareholders.
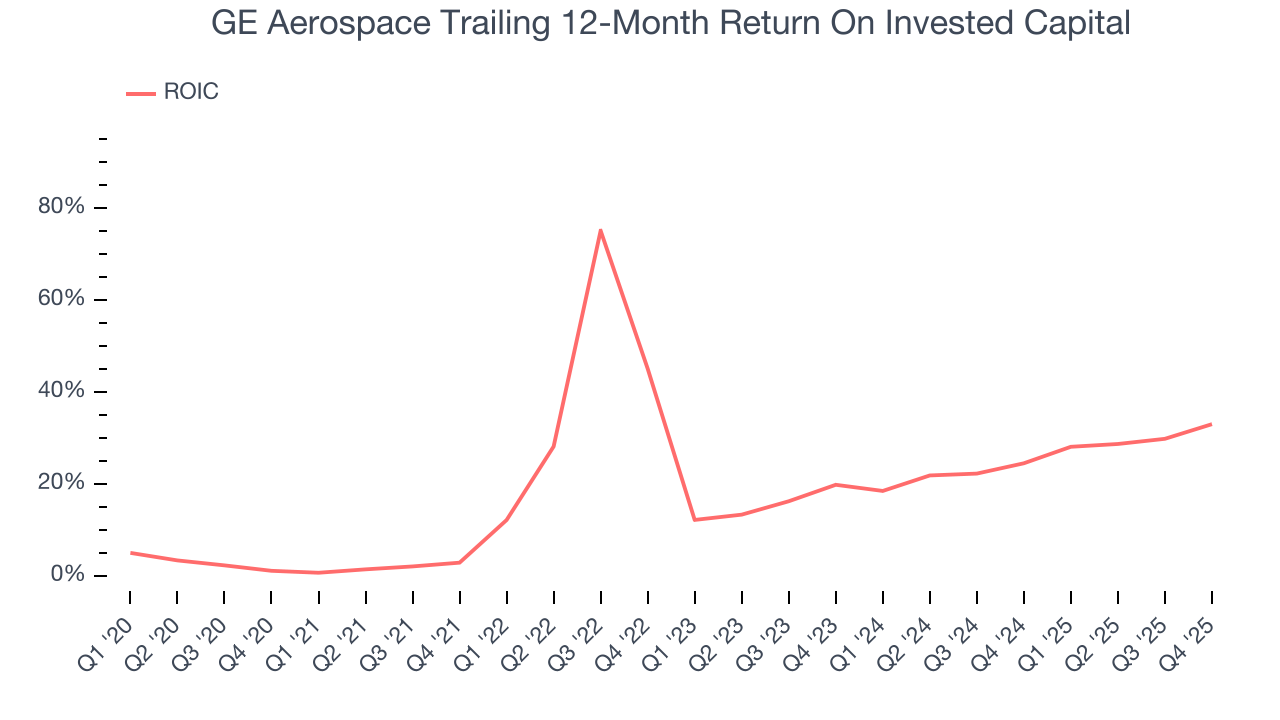
We like to invest in businesses with high returns, but the trend in a company’s ROIC is what often surprises the market and moves the stock price. Fortunately, GE Aerospace’s ROIC averaged 4.8 percentage point increases over the last few years. This is a great sign when paired with its already strong returns. It could suggest its competitive advantage or profitable growth opportunities are expanding.
11. Key Takeaways from GE Aerospace’s Q4 Results
We were impressed by how significantly GE Aerospace blew past analysts’ revenue expectations this quarter. We were also glad its full-year EPS guidance exceeded Wall Street’s estimates. Zooming out, we think this was a good print with some key areas of upside. The market seemed to be hoping for more, and the stock traded down 1.8% to $312.67 immediately after reporting.
12. Is Now The Time To Buy GE Aerospace?
Updated: January 22, 2026 at 6:53 AM EST
The latest quarterly earnings matters, sure, but we actually think longer-term fundamentals and valuation matter more. Investors should consider all these pieces before deciding whether or not to invest in GE Aerospace.
There are numerous reasons why we think GE Aerospace is one of the best industrials companies out there. For starters, its revenue growth was exceptional over the last five years. And while its low gross margins indicate some combination of competitive pressures and high production costs, its powerful free cash flow generation enables it to stay ahead of the competition through consistent reinvestment of profits. Additionally, GE Aerospace’s impressive operating margins show it has a highly efficient business model.
GE Aerospace’s P/E ratio based on the next 12 months is 45.2x. There’s no doubt it’s a bit of a market darling given the lofty multiple, but we don’t mind owning an elite business, even if it’s expensive. Investments like this should be held patiently for at least three to five years as they benefit from the power of long-term compounding, which more than makes up for any short-term price volatility that comes with high valuations.
Wall Street analysts have a consensus one-year price target of $354.82 on the company (compared to the current share price of $312.67).






